Explore AI ethics and regulations, their impact on businesses, and the future of responsible AI development with real-world examples and insights.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has rapidly evolved from a futuristic concept to a transformative force reshaping industries, economies, and societies. From personalized recommendations on e-commerce platforms to life-saving medical diagnostics, AI is everywhere. However, with such vast potential comes equally significant responsibility. Questions surrounding AI ethics and regulations have become central to global discussions on technology governance. How do we ensure AI systems remain transparent, unbiased, and accountable? What role should governments, businesses, and individuals play in creating ethical AI frameworks?
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of AI ethics, the evolving landscape of AI regulations, global initiatives, and how businesses can navigate this complex environment responsibly.
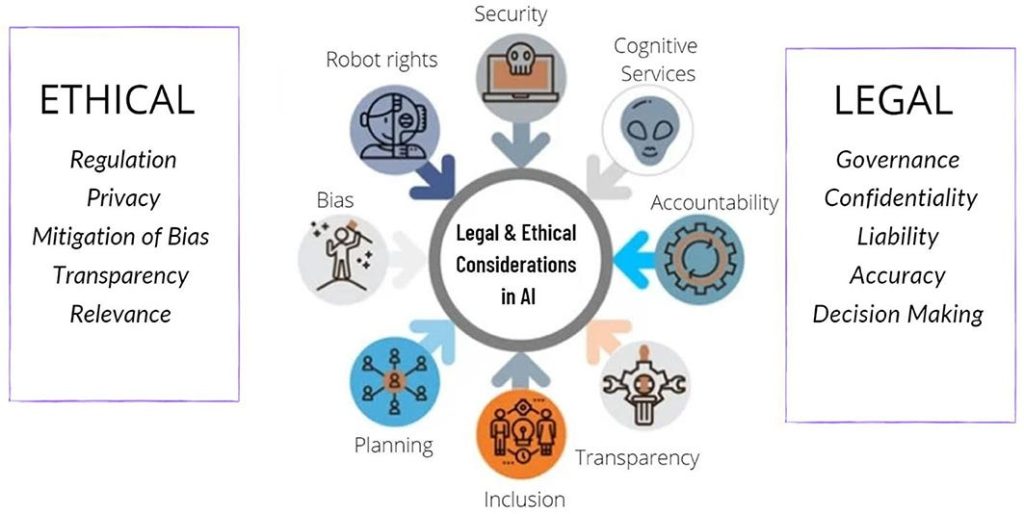
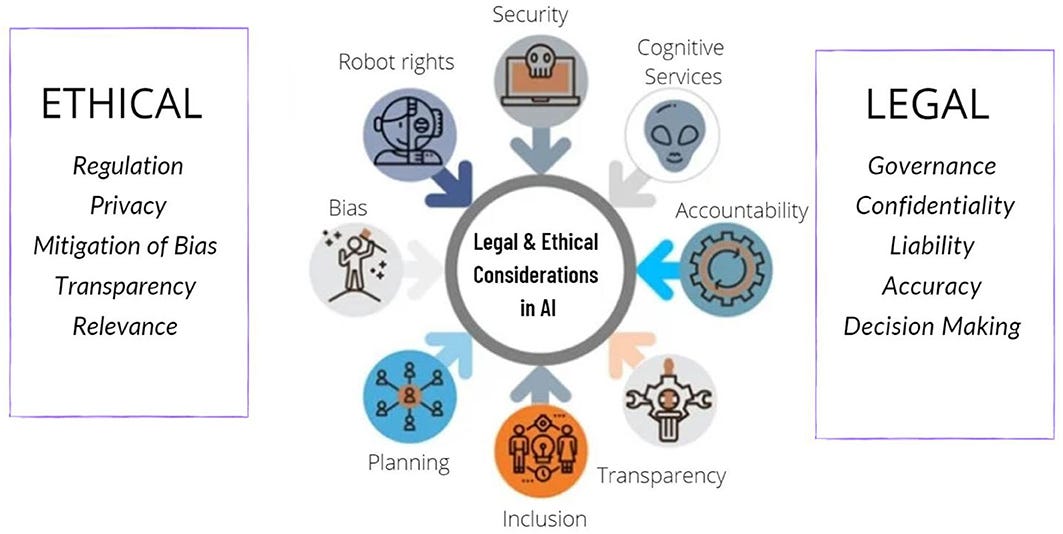
Why AI Ethics Matters
AI is powerful—but without proper oversight, it can also be harmful. Ethical concerns around AI are not hypothetical; they are already affecting society in multiple ways.
Key Ethical Challenges in AI
- Bias and Discrimination
- AI systems trained on biased data can perpetuate or even amplify inequalities. For example, recruitment algorithms have shown gender bias, favoring male applicants over equally qualified women.
- Privacy and Data Protection
- AI thrives on large datasets, but without proper safeguards, it risks violating user privacy and exposing sensitive information.
- Transparency and Explainability
- Many AI models, especially deep learning systems, operate as “black boxes.” This lack of explainability raises concerns about accountability when decisions go wrong.
- Job Displacement
- Automation powered by AI threatens traditional job roles, particularly in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and customer service.
- Security Risks
- AI can be misused for malicious purposes such as deepfakes, cyberattacks, and autonomous weapons.
By addressing these ethical concerns, businesses and policymakers can create AI systems that are not only innovative but also trustworthy.
The Role of AI Regulations
While ethics provides a moral compass, regulations establish legal boundaries. Governments worldwide are recognizing the need to regulate AI in ways that encourage innovation while protecting citizens.
Why Regulations Are Necessary
- Preventing Harm: Ensures AI does not compromise safety, privacy, or fundamental rights.
- Building Trust: Helps users and businesses feel confident in adopting AI solutions.
- Promoting Fair Competition: Prevents monopolistic practices by tech giants dominating AI innovation.
- Encouraging Global Standards: Creates consistency in cross-border AI applications and data usage.
Global AI Regulatory Landscape
Different regions are adopting unique approaches to AI governance.
European Union (EU) – AI Act
The EU AI Act is one of the most comprehensive regulatory frameworks to date. It categorizes AI systems into risk levels (unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal). High-risk systems, such as AI used in healthcare or law enforcement, face strict compliance requirements.
United States – Sectoral Approach
The U.S. follows a more industry-specific regulatory model, focusing on guidelines rather than overarching laws. Agencies such as the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) provide oversight in areas like consumer protection and data privacy.
China – State-Driven Regulations
China emphasizes state control, mandating strict oversight on algorithms used for content moderation, recommendation systems, and security applications.
Other Initiatives
- OECD Principles on AI – Promoting fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- UNESCO Recommendation on AI Ethics – A global standard for human rights-focused AI development.
How Businesses Can Adapt to AI Ethics and Regulations
For organizations leveraging AI, compliance with ethical guidelines and regulations is not optional—it’s a strategic necessity.
Practical Steps for Businesses
- Conduct AI Audits: Regularly evaluate algorithms for bias, fairness, and transparency.
- Establish Ethical AI Policies: Define company-wide standards for AI use.
- Prioritize Explainability: Choose interpretable models whenever possible.
- Ensure Data Governance: Adopt strict protocols for data collection, storage, and usage.
- Train Employees: Educate teams on AI ethics, privacy, and regulatory compliance.
Benefits of Responsible AI Adoption
- Enhanced brand reputation and consumer trust.
- Reduced legal and compliance risks.
- Improved innovation opportunities through transparent and fair practices.
- Competitive advantage in markets with growing regulatory scrutiny.
The Future of AI Ethics and Regulations
As AI continues to advance, the regulatory landscape will evolve as well. Emerging technologies like generative AI, autonomous vehicles, and AI-driven healthcare will require even more nuanced rules. We are likely to see:
- Stronger international cooperation on AI governance.
- Stricter rules for AI accountability and liability.
- Wider adoption of AI ethics certifications for businesses.
- Growing emphasis on human-centered AI design.
For businesses and policymakers, staying ahead of these developments is crucial.

Conclusion
AI is not inherently good or bad—it reflects the intentions of its creators and users. The challenge lies in building frameworks that harness AI’s potential while minimizing its risks. By prioritizing AI ethics and regulations, we can ensure that AI remains a force for positive transformation rather than unchecked disruption.
As a business leader, policymaker, or technology enthusiast, the responsibility to shape ethical AI falls on all of us. The future of AI will not only be measured by its capabilities but also by its fairness, transparency, and accountability.