Introduction
If you’ve ever watched financial news or opened a trading app, you’ve probably seen stock charts filled with lines, candles, and numbers. At first glance, they can feel overwhelming. But once you know how to read stock charts, they become powerful tools for understanding market trends, spotting opportunities, and making informed trading decisions.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essentials of reading stock charts—from chart types and timeframes to technical indicators and patterns—so you can approach investing with confidence.
Why Learning to Read Stock Charts Matters
Stock charts provide a visual representation of price movements over time. Rather than guessing, investors use charts to:
- Identify entry and exit points.
- Spot long-term trends and short-term momentum.
- Compare performance across sectors or individual stocks.
- Make informed choices instead of emotional decisions.
👉 If you’re just starting, you may also want to review our article on [how to start day trading for beginners].
Types of Stock Charts
1. Line Charts
The simplest type, line charts connect closing prices over a specific timeframe.
- Best for: Beginners and long-term investors.
- Limitations: Does not show intraday movements like highs, lows, or open prices.
2. Bar Charts
Bar charts (OHLC—Open, High, Low, Close) show more detail than line charts.
- Advantages: Provide insights into daily volatility.
- Example: A tall bar indicates higher volatility, while a short bar shows stability.
3. Candlestick Charts
The most popular format among traders, candlesticks visualize price action with “bodies” and “wicks.”
- Green/White candles: Price closed higher than it opened (bullish).
- Red/Black candles: Price closed lower (bearish).
- Wicks: Show highs and lows during the period.
👉 For real-time practice, platforms like TradingView and Yahoo Finance offer free charting tools.
Understanding Stock Chart Timeframes
Charts can display data over various periods. Choosing the right timeframe depends on your trading style:
- 1-Minute/5-Minute charts: For day traders watching short-term moves.
- Daily charts: Best for swing traders holding positions days to weeks.
- Weekly/Monthly charts: Ideal for long-term investors analyzing trends.
Tip: Always check multiple timeframes to get both the “big picture” and short-term context.
Key Elements of a Stock Chart
1. Price Axis
The vertical axis shows price levels. Tracking how prices move across time helps spot support (price floor) and resistance (price ceiling).
2. Volume Bars
Volume indicates how many shares were traded.
- High volume: Confirms strong interest in the move.
- Low volume: Suggests weak conviction or lack of participation.
3. Moving Averages
A moving average smooths out price fluctuations to show trends.
- 50-day Moving Average (short to mid-term trend).
- 200-day Moving Average (long-term trend).
Crossovers often signal trend shifts.
4. Indicators and Oscillators
Some popular ones include:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): Overbought (>70) or oversold (<30).
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Measures momentum and potential trend reversals.
- Bollinger Bands: Highlight volatility and potential breakouts.
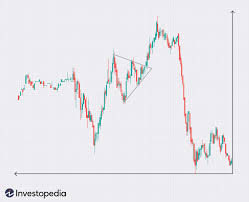
Reading Chart Patterns
Patterns give traders clues about future price action.
Common Bullish Patterns
- Cup and Handle: Suggests continuation of an uptrend.
- Ascending Triangle: Breakout potential at resistance level.
Common Bearish Patterns
- Head and Shoulders: Indicates possible trend reversal downward.
- Descending Triangle: Suggests breakdown at support level.
Neutral/Indecision Patterns
- Doji Candlestick: Market indecision, potential reversal.
- Rectangle Pattern: Price consolidates before breakout.

Practical Steps for Beginners
- Start with Line Charts – Build confidence before moving to candlesticks.
- Focus on One Indicator – Too many tools can cause confusion. Start with moving averages.
- Track Volume – Use it as confirmation for price moves.
- Practice on a Demo Account – Platforms like Thinkorswim or Interactive Brokers offer free practice.
- Keep a Trading Journal – Record your chart observations and outcomes to learn faster.
👉 For more insights on risk control, read our guide on [risk management tips for traders].
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overloading with Indicators: Stick to a few reliable ones.
- Ignoring Market Context: News, earnings, and global events affect charts.
- Chasing Every Move: Patience is key. Wait for confirmation before acting.
- Not Practicing Enough: Reading charts is a skill—develop it through repetition.
Tools & Resources for Chart Analysis
- Free Tools: Yahoo Finance, TradingView, StockCharts.com
- Broker Platforms: Fidelity, TD Ameritrade’s Thinkorswim, E*TRADE
- Learning Resources: Investopedia’s charting tutorials, financial podcasts, and YouTube trading educators
👉 If you’re also evaluating where to trade, check our comparison of [best stock trading platforms 2025].
Conclusion
Learning how to read stock charts is one of the most valuable skills for investors and traders. By mastering chart types, timeframes, and key indicators, you gain insights into market psychology and can make more informed decisions.
Whether you’re investing for the long haul or trading daily swings, remember that charts are tools—not guarantees. Combine chart analysis with solid risk management and ongoing learning to maximize success.
Action Step: Open a free charting tool today, experiment with different chart types, and start practicing by analyzing stocks you already follow.
Internal Links:
- [How to start day trading for beginners]
- [Risk management tips for traders]
- [Best stock trading platforms 2025]
External Links:
- TradingView for real-time charting
- Yahoo Finance for free stock data and charts